The Bladed tower model is a linear finite element model, but the foundations can be defined with non-linear lookup tables. How do these two models work together to model the non-linear foundation behavior? How is the non-linear part of the curve used?
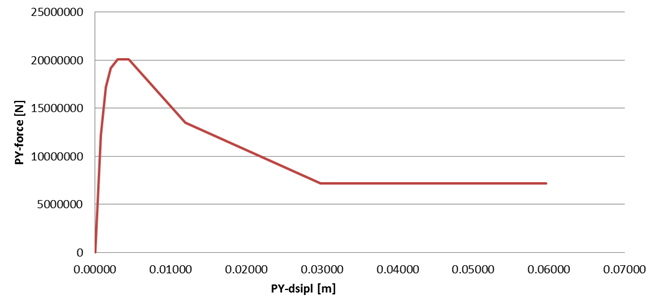
The initial linear slope of the curve is calculated and included directly in the structural model. The linear slope is therefore included in modal analysis. During a simulation, the non-linear part of the force is applied to the model as an external load.
Some more details of the interactions between the linear modal model and the non-linear foundation model are given below:
At a certain time step, we know the positions and velocities of all of the nodes calculated from modal dynamics, and we want to find the accelerations, in order that we can step forwards in time. The accelerations depend on the applied loads, modal mass, modal stiffness and modal damping properties.
In order to get an accurate non-linear foundation reaction force to apply to the structural model, we need to calculate the support structure deflections more accurately than a modal deflection solution. To do this, we can calculate deflections by applying loads to the full finite element stiffness matrix. This type of calculation is a static deflection calculation but includes “d’Alembert” forces which are inertia forces associated with accelerating mass and inertia, as well as external applied loads (e.g. from non-linear foundations).
One difficulty in this approach is that the applied loads to calculate the FE deflections include loads that depend on deflections (e.g. from non-linear foundations) and acceleration (i.e. inertia forces) – so iteration is required at each time step to find the correct solution.
During this iteration, the deflections, accelerations and applied loads at the foundation nodes are iterated until a solution is found. Each time the applied load is updated, these forces are applied to the original modal model to calculate the overall structural response (accelerations) until convergence is found. The foundation deflections will be different in each iteration due to the different applied loads (from foundations and inertia forces).
When convergence is achieved for the foundations, the known foundation forces are applied to the modal model, and the time-step integration proceeds as normal.