Bladed doesn't have a built-in breaking wave model. However, offshore turbine modelling may require breaking waves to be considered.
Also, Bladed may sometimes exit with an error message of "ERROR: Wave height greater than breaking wave height." What to do in this situation?
Versions of Bladed affected: All versions
Date article last updated: 15 June 2023
Breaking waves cannot be modelled explicitly in Bladed. In any case, accurate modelling of breaking wave is not straightforward and all practicable engineering models are only approximations.
Normally, when a breaking wave is present, we advise to use the Constrained Wave option, choosing the "Stream Function" option, not the linear wave:
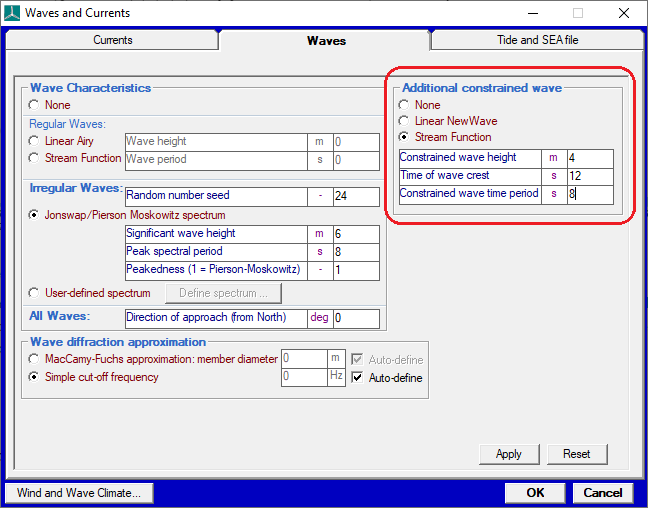
Next, adjust the height of the constrained wave by trial and error until you have the steepest wave that just falls below breaking steepness. The stream function theory can give some unrealistic results when operating too close to its limits. Therefore we advise that you carry out a visual inspection of the surface elevation time history, as well as the water particle kinematics outputs. Any problems with the model in this marginal situation will usually be obvious from the results, in which case you should reduce the wave height accordingly.
The stream function wave will provide a partial solution to the wave loading, but an additional load time history may be applied as well in order to approximate the additional loading from the breaking wave. Guidance can be found in Annexes B and C of the offshore standard IEC 61400-3-1 (2019 edition). Specifically, Section B-4 contains a general discussion of breaking waves and C-4 describes an empirical formula for calculating the additional load due to wave impact forces (slap and slam loading) which can be applied to Bladed using the Point Loading function, timed to coincide with the arrival of the constrained wave peak.